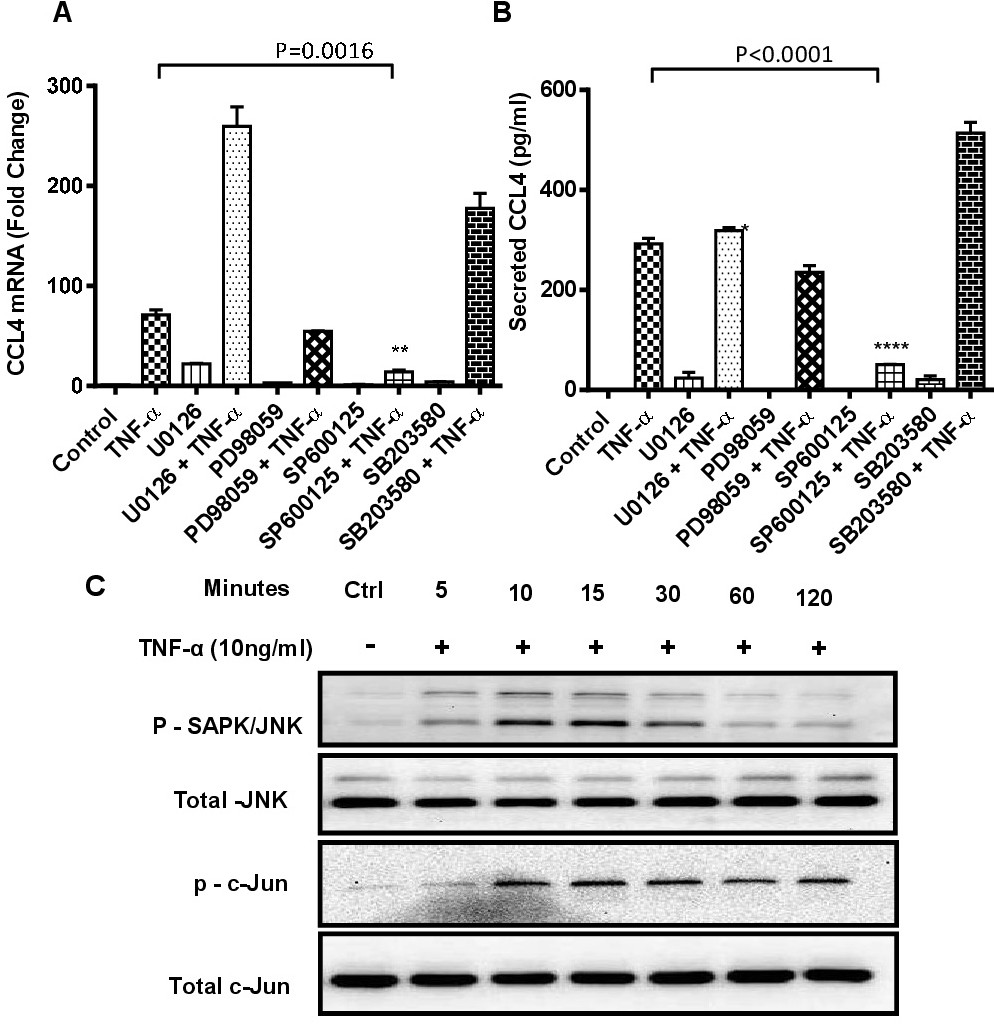
Fig. 3. TNF-α-induced CCL4 expression is abrogated by treatment with chemical inhibitor of SAPK/JNK pathways. THP-1 monocytic cells were pretreated with chemical inhibitors of MAPK (U0126, PD98059), p38 (SB203580) or SAPK/JNK (SP600125) pathways using concentrations as recommended by the manufacturer and cells were incubated at 37°C for 1 hr. Later, cells were stimulated with TNF-α (10ng/ml) and incubated for 24 hrs. Cells and culture media were collected and CCL4 mRNA in cell lysates and protein expression in cell supernatants were determined using real-time RT-PCR and ELISA, respectively. The data show that CCL4 (A) gene (P=0.0081) and (B) secreted protein (P=0.0021) expression were significantly suppressed in cells pretreated with SAPK/JNK pathway inhibitor SP600125 compared to mock-treated controls. However, no significant suppression was observed with MAPK and p38 inhibitors. To analyze TNF-α-induced protein phosphorylation, cells were incubated with TNF-α (10ng/ml) and cell samples were collected at 5, 10, 15, 30, 60, and 120 min. Mock treated cells served as control. Cell lysates in RIPA buffer were calibrated for protein concentration, resolved by SDS-PAGE and SAPK/JNK and c-Jun protein phosphorylation was determined using specific antibodies against phosphorylated and total proteins. (C) The data show that TNF-α treatment of THP-1 human monocytic cells induces phosphorylation of SAPK/JNK as well as c-Jun.